There has been a growing movement towards sustainability and environmental consciousness in recent years, and reverse logistics is one area seeing significant change.
As consumers become more aware of the negative impact of their choices on the planet, they are increasingly seeking out products that are eco-friendly and sustainable.
This trend forces businesses to adapt their practices to meet the modern consumer’s demands.
Also known as returns management, reverse logistics return goods to the supply chain after selling them.
For businesses, reverse logistics can be a complex and costly process.
However, in the age of sustainability, it is essential to ensure that products are reused or recycled.
In this article, we will explore the concept of reverse logistics in more detail, looking at its benefits and challenges for businesses.
What Is Reverse Logistics?
Traditional logistics refers to moving goods from the point of manufacture to the end of the sale. In contrast, reverse logistics refers to returning goods from the point of purchase to the point of manufacture. This return flow can happen for several reasons, such as damaged or defective merchandise, incorrect orders, or simply because a customer has changed their mind.
For this reason, companies need to have a well-organized reverse logistics system to handle returned items efficiently.
At a basic level, the reverse logistics process involves four main steps: receiving returns, evaluating them, repairing or refurbishing them (if necessary), and then either restocking them or disposing of them.
However, this process can quickly become quite complex depending on the type and quantity of returned items.
For example, some companies may offer customers a refund or store credit rather than replacing the item; others may need to coordinate with suppliers to source replacement parts, and others may need to negotiate with manufacturers to dispose of Hazmat materials.
As you can see, managing a reverse supply chain is no easy task—but it’s one that all successful businesses must learn how to do.
Types of Reverse Logistics
There are a few different types of reverse logistics that businesses can use, depending on the products they sell and the needs of their customers. By understanding the different types of reverse logistics, companies can ensure that they return products promptly and efficiently.
Here are the different types of customer logistics that you should know:
Returns
Returns are a type of reverse logistics that returns products, services, or items to the customer or the company that supplied them. Returns can occur for various reasons, including defective products, incorrect orders, or buyer’s remorse.
In many cases, customers must obtain a return authorization from the company before returning an item.
Once the company receives the item, they inspect it to ensure it meets quality standards and for reselling. It is typically disposed of if the thing is not up to par.
Delivery Failure
Any time a company delivers products or services to a customer and fails to meet the delivery terms, it is considered a delivery failure. Delivery failure can happen for various reasons, such as an item being damaged in transit, delivered to the wrong address, or delayed beyond the promised delivery date.
While delivery failures are undesirable from the customer’s perspective, they can also be costly for businesses. In addition to the financial cost of replacing or repairing damaged goods, companies also risk losing customers due to poor service.
As a result, you must carefully manage delivery failures as part of any company’s reverse logistics strategy.
Remanufacturing and Refurbishment
Remanufacturing and refurbishment are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different processes. This process is taking a used product and restoring it to like-new condition. Remanufacturing can replace worn or damaged parts, reset factory defaults, and run comprehensive tests.
On the other hand, refurbishment refers to bringing a product’s appearance up to par. Refurbishment can involve anything from cosmetic touch-ups to more extensive repairs.
The manufacturer or an authorized repair center typically provides these services.
Unsold Goods
Unsold goods refer to products a customer has returned or products a company has taken back from the customer. In other words, unsold goods are items that are no longer in possession of the customer.
There are various reasons why products become unsold goods.
For example, the customer may not have been satisfied with the quality of the product or may have changed their mind about the purchase.
Products sometimes become unsold goods because they are damaged or defective. Whatever the reason, unsold goods must be carefully managed to minimize losses for the company.
End-of-Life
The term “end-of-life” refers to the point at which a product is no longer profitable or valuable to a customer. At this stage, businesses have a few options: they can continue to support the product, sell it for parts, or recycle it.
When products are returned to the manufacturer, they can be repaired, refurbished, or recycled. This prolongs the product’s lifespan and keeps it out of landfill.
In addition, by returning products directly to the manufacturer, businesses can avoid the cost and hassle of managing their returns process.
Rentals and Leasing
Rentals and leasing are reverse logistics methods that offer several benefits for both businesses and customers. Companies can save on inventory costs and storage space by renting or leasing products instead of purchasing them outright.
On the other hand, customers can enjoy using items without the commitment of owning them.
Additionally, rentals and leasing can help to promote sustainability by prolonging the life cycle of products.
Repairs and Maintenance
Repairs and maintenance are imperative to any product’s or service’s life cycle. They enable customers to keep products and services in excellent working condition, reducing waste and saving the company money.
In addition, repairs and maintenance show the customer that the company stands behind its products and is committed to providing excellent customer service.
By investing in effective repairs and maintenance programs, companies can ensure that their products remain in good condition and that their customers are satisfied.
How Reverse Logistics Benefit Your Business
Knowing the different types of reverse logistics can make the task look challenging. However, reverse logistics is rewarding when done correctly. Here are the six real benefits that you would get with reverse logistics:
Reduced Costs
One of the most immediately apparent benefits of reverse logistics is reduced costs.
When you can effectively manage the return of goods and materials, you can avoid the waste that often comes with simply disposing of them.
In addition, returning products to the supplier can often receive a partial refund or credit applied to future purchases.
Better Customer Retention
Another vital benefit of reverse logistics is better customer retention.
If a customer is unhappy with a product they have purchased from your business, managing the return promptly and efficiently can go a long way in ensuring that they remain a customer.
Additionally, suppose you can quickly resolve any issues they may have had with the product. In that case, they will be more likely to give your positive business reviews, which can help attract new customers.
Actionable Product Data
In addition to reducing costs and improving customer retention, another critical benefit of reverse logistics is actionable product data.
When products are returned to your business, you have an opportunity to examine them and determine what went wrong. This information can then be used to improve your manufacturing or sourcing processes so that future products are of higher quality. Furthermore, you can change your marketing or sales strategies by understanding which products are returned most frequently.
Better Service
Businesses can also improve their customer service strategy by tracking products throughout the post-purchase journey and collecting customer feedback.
This information can identify areas where customers are having difficulty and make changes accordingly.
Additionally, this data can be used to develop new customer service policies or procedures to improve the overall customer experience.
Reduced Waste
Another benefit of reverse logistics is that it helps businesses reduce waste.
Product data gathered through tracking can be used to identify areas where a business’s packaging or manufacturing process may be causing unnecessary waste. Companies may also reduce landfill waste by reusing or refurbishing components.
Improved Brand Image
Last but not least, utilizing reverse logistics can also improve your brand image in the eyes of consumers. By having a well-run returns process, you will be viewed as a company that is easy to do business with and cares about its customers. This improved brand image will ultimately lead to more sales and continued growth for your business.
Reverse Logistics Challenges
Every supply chain management strategy has its own set of unique challenges.
The main issue facing businesses when it comes to reverse logistics is profitability. Returns are often seen as a cost to be minimized rather than an opportunity to add value. However, reverse logistics can be profitable with the right approach. By focusing on customer satisfaction and using returns to gather data and improve operations, businesses can use reverse logistics to their advantage.
Another issue is the lack of an appropriate infrastructure which often incurs high costs and inefficiencies. In many cases, businesses are forced to either absorb the cost of customer returns or pass it on to the consumer through higher prices. This puts companies at a competitive disadvantage and often leads to customer satisfaction issues. As such, businesses need to find ways to improve the efficiency of their returned logistics to stay competitive and keep customers happy.
In the following few sections, we will look at implementing reverse logistics processes to benefit your business.
We’ll also discuss some challenges you may face when implementing these processes and how to overcome them. Reverse logistics can be complex and costly, but the right approach can also be a valuable tool for your business.
The Five R’s of Reverse Logistics
So, how can you overcome these challenges? The Five R’s of reverse logistics is an excellent place to start when you’re looking to improve your reverse logistics.
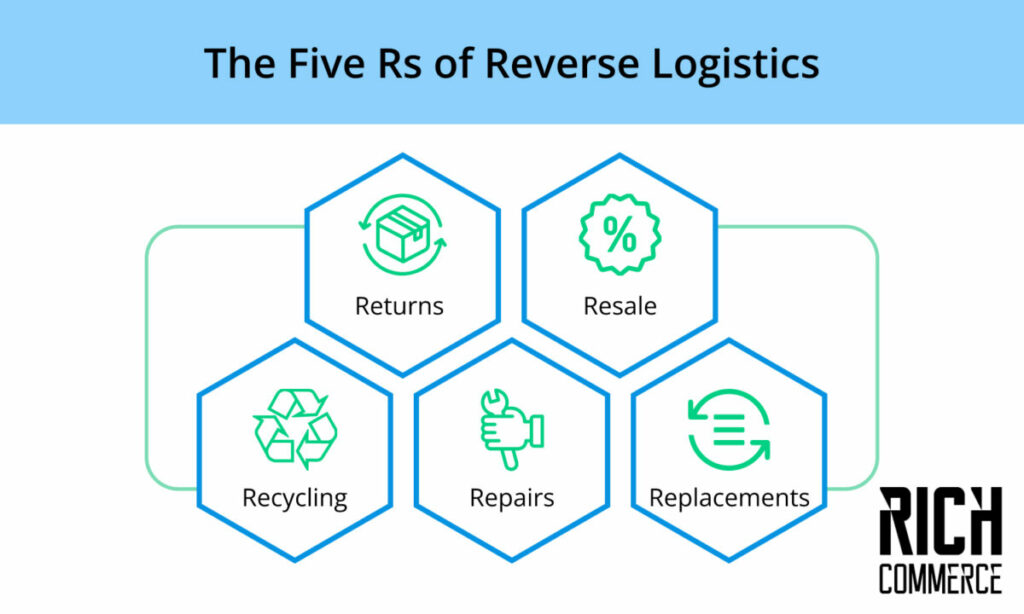
Returns
The first R is “Returns.” A transparent and efficient return policy is crucial because it will directly impact customer satisfaction levels. Make sure you track the monthly returns you receive to identify any patterns or trends. You should also follow the reasons for returns so that you can take steps to prevent them in the future. For example, if you notice that a high percentage of returns are due to damaged goods, you may need to reconsider your packaging strategy.
A satisfied customer is more likely to make repeat purchases from your store, so you must do whatever you can to minimize returns. Key metrics to track include:
- Number of returns per month
- Reason for return
- Cost of return shipping
- Customer satisfaction levels after a return is processed
Resale
The second R is “Resale.” Businesses often resell returned items instead of throwing them away or destroying them.
This can be a great way to recoup some of your losses and reduce waste simultaneously. However, tracking the percentage of returned items that are successfully resold is vital to determine whether or not it’s worth your while. Other key metrics to track include
- Percentage of returned items that are resold
- The average selling price of returned items
- Cost of repair or replacement (if necessary) before an item can be resold
Recycling
The third R is “Recycling.” Many products can be recycled instead of thrown away, which is good for the environment and your bottom line. Make sure you have a system for recycling all eligible items. Key metrics to track include
- Percentage of returned items that are recycled
- Weight or volume of recycled materials
- Cost savings from the recycling program
Repairs
The fourth R is “Repairs.” If an item is returned because it’s defective or damaged, you may be able to repair it instead of replacing it entirely. This can save you time and money in the long run. Key metrics to track include
- Number of repairs per month
- Reason for repair
- Cost of repair
- Customer satisfaction levels after the repair is completed
Replacements
The fifth and final R is “Replacements.” In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to replace an item rather than try to repair it. As with repairs, tracking the number of replacements, you make every month and the reason for each sub is essential. Other key metrics to track include
- Number of reserves per month
- Reason for replacement
- Cost of replacement
- Customer satisfaction levels after a replacement is received
Reverse Logistics Process
Next, you’ll have to optimize your reverse logistics process. This is imperative for businesses that want to reduce waste and carbon footprint. Here’s how you do it:
Process the Return
The first step in setting up an efficient reverse logistics process is understanding what needs to happen when a product is returned.
This may seem obvious, but it’s essential to have all the steps mapped out so you can determine where there might be bottlenecks or other problems. Once you understand the return process, you can start working on ways to make it more efficient.
Categorize the Return
One way to make your reverse logistics process more efficient is to streamline the process for categorizing returns.
This will help you more quickly identify which items can be reused or resold and which need to be disposed of. By clearly understanding what needs to happen to each type of return, you can avoid wasting time and resources on processing returns that ultimately end up in the trash.
Designate Return Areas
Another way to improve the efficiency of your reverse logistics process is to designate specific areas for returned items.
This will help you avoid having returns thrown into random piles around your warehouse or office, making it difficult to find what you’re looking for when you need it. Designating return areas will also help you more easily keep track of items that need to be processed so that nothing gets lost in the shuffle.
Recycling and Waste Disposal
Finally, you need to have a plan to properly dispose of waste and recycle what you can. This is particularly important if you sell perishable goods or items that cannot be resold. By developing a method to dispose of these items, you can minimize waste and keep your operation running smoothly.
Monitoring the Reverse Logistics Flow
The last thing you can do to optimize your reverse logistics is monitoring. There are several factors that you should take into account when monitoring your reverse logistics flow:
Volume
The volume of returns is a good indicator of customer satisfaction. If a merchant sees a high volume of returns, it may indicate a problem with the product or customer service. By analyzing the importance of returns, merchants can identify patterns and take steps to address them.
Cost Comparison
Returns can be costly for merchants, so it’s essential to understand the cost comparison of returning vs. replacing products. In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to replace the product rather than return it. By understanding the cost comparison, merchants can make informed decisions about how to handle returned products.
Product Condition
The condition of returned products is also vital for eCommerce merchants to monitor. In some cases, products are returned because they are damaged or defective. In other cases, products are returned simply because the customer changed their mind or no longer needs the product.
By understanding why products are being returned, merchants can take steps to avoid damages and defects and also ensure that they’re providing accurate descriptions of their products online.
Financial Value
The financial value of returned items is another important consideration for eCommerce merchants. In many cases, returned items are sold at a discount or not sold at all. By understanding the financial value of returned items, merchants can determine whether it’s worth it to accept returns or not.
Errors
Finally, eCommerce merchants need to monitor errors in their return process. Common mistakes include lost items, incorrect refunds, and delays in processing returns. By understanding where mistakes occur in their approach, merchants can take steps to avoid them in the future.
Reverse Logistics Made Easy With Rich Returns
Reverse logistics is a complex process that can be difficult to manage for businesses of all sizes. However, when done correctly, reverse logistics can provide many benefits, including reducing waste, becoming more sustainable, and even turning a profit.
Rich Returns is the perfect solution if you’re looking for a platform that will help you streamline your reverse logistics process. We offer a Shopify Returns & Exchanges Management Platform that makes it easy to manage returns and exchanges quickly and efficiently.
Start your free trial and see how we can help optimize your reverse logistics process and improve your bottom line.


